Nanomaterials for Targeted Drug Delivery & Photothermal Therapy
Fortis Life Sciences uses proprietary nanoparticle manufacturing techniques to allow medical devices and therapeutic products to be developed and commercialised at pace. Unlike many of our competitors, we specialise in both nanomaterials and GMP manufacturing.
We help clients develop and market high-impact, nano-enabled therapeutic products using our diverse expertise, which covers nanoparticle fabrication and biofunctionalisation for targeted delivery, controlled-release, photothermal therapy, and more.
Fortis’ CDMO services include research (proof-of-concept synthesis and characterisation), development (optimisation, scale-up, process development and validation), transfer to manufacturing, and scaled manufacturing.
Key nanoparticle platforms
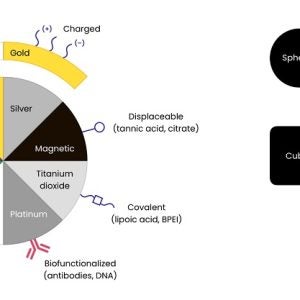
- Metal nanoparticles
– Gold, silver and more
– Spheres, rods and more
– Silica-shelled metal cores - Silica nanoparticles
– Mesoporous
– Microporous/solid - Polymer nanoparticles
– PLGA, PLA
– Lipid
Application areas for nanoparticles
- Targeted delivery: Gold, silica, magnetite, and polymer (PLGA) nanoparticles have all demonstrated efficacy in targeted drug delivery applications due to their ability to deliver a therapeutic agent rapidly and accurately.
- Theranostics: Nanoparticles solve the unique combinations of challenges presented by the emerging area of theranostics. By rapidly and accurately accumulating on targets of interest, they can gather biochemical and morphological information about the target at the same time as delivering a therapeutic compound efficiently.
- Photothermal therapeutics: The unique plasmonic properties of metallic nanoparticles such as gold nanoshells, gold nanorods, and magnetite nanoparticles make them very suitable for photothermal therapeutic applications ranging from topical treatments to cancer therapies.
- Gene delivery: There has recently been a rapid growth in the exploration of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as platforms for gene delivery. The tunable particle sizes, pore sizes, and pore geometries of mesorporous silica nanoparticles make them ideal for the targeted delivery of therapeutic genes.
Fortis’ production method
- Design feasibility
– Concept: Determining the product’s feasibility, identifying the scope of the project
– Research and development: Defining user needs and identifying the corresponding design inputs - QMS design controls
– Design development: Identifying the stages, activities, responsibilities, resources and verification methods for design and development
– Product development: Establishing a product design with detailed associated specifications - Transfer to manufacturing
– Verification: Examining objective evidence to confirm the product meets specified requirements
– Validation: Obtaining objective evidence to assure that the product meets the intended user needs - Custom and CGMP manufacturing
– Design transfer: Transferring the process from development to commercial-scale manufacturing; ensuring all design requirements and product specifications can be met in commercial production; identifying potential problems before transferring to commercial GMP