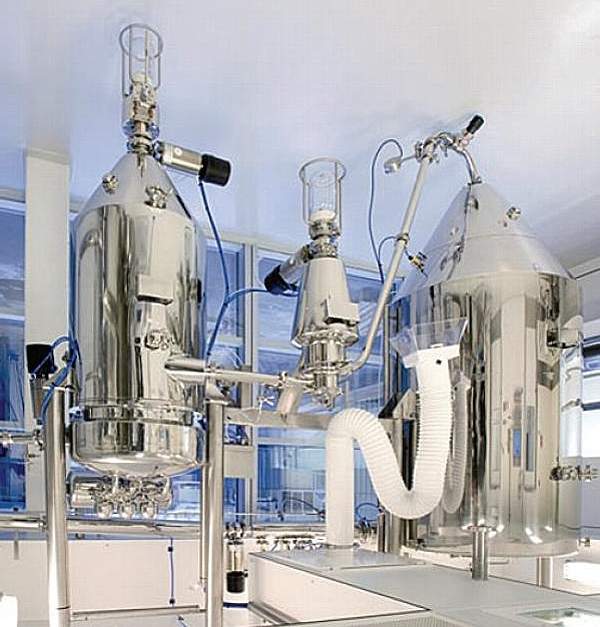
GEA Niro’s GMP pharmaceutical spray drying facility is part of the company’s Test Centre located in Copenhagen, Denmark. Opened in April 2010, the state-of-the-art facility has a clean room, with a class rating of 100,000.
The facility enables testing of spray drying process and contract manufacturing of materials used in clinical trials. It is approved by the Danish Medicines Agency and is compliant with European Union standards for production of investigational medicinal products (IMP).
GEA Niro’s Test Centre includes more than 40 pilot plants, apart from the pharmaceutical spray drying facility. These plants provide several facilities for developing processes for use in the chemical, dairy and food sectors.
The Test Centre is staffed with experienced members who work with consumers on a case-to-case basis to develop optimal production processes.
Advantages of GEA Niro’s pharmaceutical spray drying facility in Denmark
GEA Niro’s facility enables pharmaceutical companies to determine if spray drying is the right technology for the manufacturing of a new drug. It includes both micro-plants to produce small samples for clinical trials and full scale plants for commercialisation of product.
Spray drying technology provides several advantages, including increased bioavailability of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), controlled release for physical protection of APIs, production of fine powders, aseptic production and production of solid dosage formulations.
The technology is a fast and effective method of particle formation and manufacture of free-flowing powders. It is already widely used in chemical and food industries and has been adapted by GEA Niro for the pharmaceutical sector.
Pharmaceutical companies can develop spray dried products without making any major investment before commercialisation of the product. The facility also reduces the time between drug development and commercial production. As a result, patients can benefit from faster availability of drugs in the market.
To further improve its spray drying technology, GEA Niro formed a partnership with BASF in February 2010, under which BASF provides synthesis services.
Manufacturing processes at GEA Niro’s Copenhagen-based Test Centre
The spray drying plant is equipped with both non-GMP and GMP facilities. The product is first refined under non-GMP conditions before being produced under GMP conditions. Non-GMP facilities include bench analysis and trials wherein DRYNETICS process technology is used to determine the correct drying process.
This technology uses just a single droplet of the product to establish the correct spray drying process.
Spray drying processes include four steps – atomisation, drying, particle formation and powder recovery. Atomisation is a process wherein the liquid product is atomised into droplets using a nozzle. The droplets are brought into contact with a gas dispenser to evaporate the liquid present. Once the liquid evaporates, a solid particle or powder is formed which is recovered. The entire process takes just a few seconds to complete.
The best spray drying process is then developed and samples are produced for technical analysis. Qualified personnel review the process to suggest any modifications, if necessary. Before GMP testing of the optimum spray drying process, it is tested on large-scale plants similar to those of the final production plant.
The GMP facility of the plant is equipped with two PHARMASD spray dryers, type PSD-1 and PSD-4, to produce the required quantity of samples. The PSD-1 spray dryer can be used for production in small quantities and PSD-4 for large scale production.
PSD-1 and PSD-4 spray dryers at the GMP facility
Spray dryers are equipped with a chamber, cyclone, bag filter, HEPA filters, condenser and electrical heaters. Type PSD-1 uses two-fluid nozzle for atomisation while PSD-2 dryer uses two atomisation techniques using a pressure nozzle and a two-fluid nozzle. Both dryers use nitrogen for drying. They operate separately and have different HVAC systems.
The spray dryers can be used for cGMP production of clinical trial materials or for commercial production. The size of the PSD-4 dryer is similar to that of an actual production facility, enabling easy transfer from testing to commercial production.