Celltrion, a joint venture between San Francisco-based Vaxgen and a group of South Korean investors, completed the construction of a new biopharmaceutical plant in Incheon, South Korea in the final quarter of 2005; validation was completed by the end of the first quarter of 2006 and the plant was in full production by mid-2006. The plant has been built at the heart of a new technology park in Songdo New City. The site has been carefully chosen for its proximity to Seoul (the capital) and the newly opened Incheon International Airport.
The plant is being used for the production of vaccines (anthrax, small pox and meningitis B) and also for the production of recombinant therapeutic proteins. VaxGen had earlier built and commissioned a smaller biopharmaceutical pilot plant (1,000l) in San Francisco; this was to be used for clinical and early commercial-scale manufacture and in a development role to the new plant in Korea.
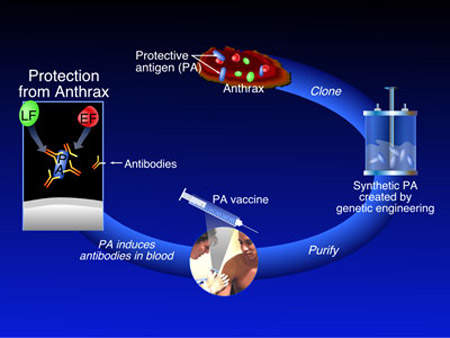
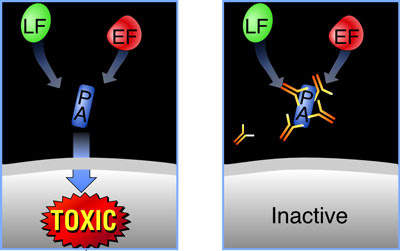
VaxGen exercised its right in February 2005 to acquire all of the shares in the US based pilot plant for $7.7m. The plant was used to train many of the Korean staff who are employed by Celltrion at the new Incheon facility and was being used to produce recombinant antigen protein Rpa102 for VaxGen’s anthrax vaccine. 75 million doses were ordered by the US government at a cost of $877.5m as part of project Bioshield but this contract was cancelled in December 2006 because of the company’s failure to meet deadlines for clinical trials.
Investors
The Celltrion ‘investment group’, founded in February 2002, included VaxGen (48%), Nexol and Nexol Biotech (13%), Korean Tobacco and Ginseng (13%), J. Stephen and Co Ventures (13%) and others (8%). The investment in the Korean plant is $85m. The contribution from VaxGen was in technology, training and knowledge transfer.
In mid-2006 VaxGen sold its stake in Celltrion to the other shareholders for $53.6m. The shares were purchased by three related Korea-based entities – Nexol, Nexol Biotech and Nexol Venture Capital – which together represented Celltrion’s largest shareholder. The shares were acquired through the exercise of an exclusive option that VaxGen granted to the Nexol entities in June 2006.
Contractors and construction
Fluor Corporation was the contractor responsible for architectural and engineering design and also procurement; the contract was awarded in November 2002. The main construction and installation contractor is Daewoo Engineering and Construction of Korea; they were also responsible for detailed engineering.
The bioreactors were designed and constructed by BioEngineering of Switzerland. The process engineering design work was shared between Daewoo and BioEngineering. Foster Wheeler was also involved in the engineering of the plant.
The equipment for the outfitting of the process side of the plant, such as filtration and chromatography, was supplied by Amersham and Millipore.
Emerson Process Management automated the large-scale biopharmaceutical manufacturing facility. Emerson provided engineering services and key components of its PlantWeb digital plant architecture to help streamline the facility’s manufacturing process, increase output and reduce costs. Emerson’s Asia Pacific Life Sciences Engineering Center in Singapore and system integrator in Korea provided engineering design, configuration, documentation, site testing, commissioning and validation support. Emerson’s PlantWeb components for Celltrion included the DeltaV digital automation system and AMS Suite of predictive maintenance software. The Audit Trail within DeltaV and AMS provides automated documentation to help meet FDA regulatory requirements of 21 CFR Part 11.
Timelines
Construction began in March 2003 and the facility was mechanically complete by early 2005. It was validated and fully cGMP compliant by early 2006, meeting all US FDA and EU EMEA requirements as a multi-product cell culture facility. The plant was in full production by mid-2006. The validation originally scheduled for January 2005 was delayed for one year to accommodate client-specific modifications at the plant.
Bioreactor facilities
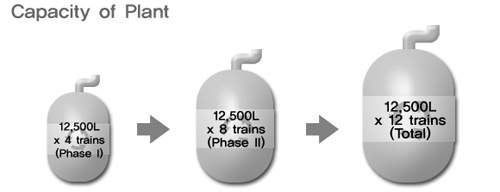
The plant includes four independent trains of bioreactors; each train comprises 20l, 100l, 500l, 2,500l inoculum seed reactors and a 12,500l production bioreactor. The 2,500l bioreactors can also be used for smaller volume clinical or commercial production and can be harvested directly as production vessels.
The bioreactors are designed for batch production but will have the capability for modification to enable perfusion culture methodology. The bioreactor trains are designed to allow more than one cell culture product at any one time to be produced. Each bioreactor system is equipped with fully automated Clean in Place (CIP) and Sterilise in Place (SIP) systems. Two fully independent inoculum preparation suites are available.
A purpose designed GMP dispensing area adjacent to the materials warehouse allows media and buffer preparation kits to be made up. Separate media and buffer preparation areas were designed with independent airlock access and CIP systems. Water for Injection (WFI) is to be used for all media and buffer preparation as well as CIP final rinses. Buffer solutions are handled in two ways – either sterile filtered and stored in sterile buffer holding tanks, or filtered and used directly. Media is sterile filtered directly into the bioreactor or for smaller batches into sterile media holding tanks.
Harvesting, purification and downstream processing
Cell separation is carried out using centrifugation (Westfalia) and depth filtration, either separately or in combination. A 15,000l sterile harvest vessel is available to hold cell culture solutions at refrigerated or ambient temperatures. The facility incorporates separate purification areas for initial purification (pre-viral inactivation) and final purification (post-viral inactivation) and bulk drug substance filtration.
All of these areas have their own service areas, i.e. access airlocks, cleaning areas and CIP systems. This is to ensure there is little possibility of contamination. Purification facilities include affinity, ion exchange, hydrophobic interaction and gel filtration chromatography as well as ultrafiltration and diafiltration. All of the processing areas have been designed to maintain operating environmental conditions of at least ISO-8 (USP-dynamic class 100,000).
Celltrion expansion
Since starting production Celltrion has signed a number of long-term contracts with large pharmaceutical companies for the contract manufacture of protein therapeutics including a 10 year contract to supply the majority of their 50,000l bioreactor capacity for the production of biopharmaceutical products (abatacept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and belatacept an immunosuppressant) for Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS).
Celltrion has also signed a 60,000l bioreactor supply contract. In order to meet the terms of these long-term contracts, and carry out research projects as well, in July 2006 Celltrion started to construct an 90,000l protein-based medicine production facility and known as Plant 2.
Physical construction of the plant has been completed and it is expected to be validated by the end of 2012. Plant 2 has six trains of 15,000l capacity of or. Production will begin in 2013 and will increase total capacity to 140,000l making it the largest biotech production facility in the world.
The company plans to build another 90,000l capacity facility, called Plant 3. Space for the new facility is already available on the same premises.
Celltrion collaborations
Celltrion is working on the development of colon cancer and breast cancer drugs in cooperation with US and European biopharmaceutical companies with the goal of developing protein-based treatment medicines, including monoclonal antibodies, in the new medicine sector.