New York-based biotech Elion Therapeutics has bagged $81m from a Series B funding round for its early-stage polyene antifungal therapy, SF001.
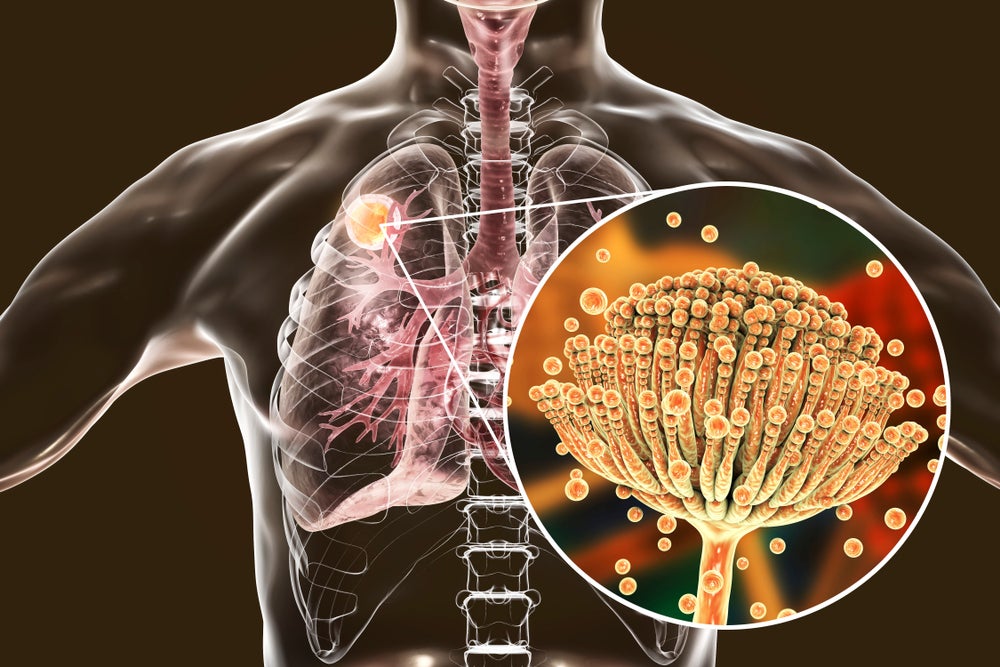
The candidate is being investigated as an early antifungal therapy for presumed invasive fungal disease and invasive aspergillosis. Last year, the drug won fast track and qualified infectious disease product (QIDP) designations from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) . The drug was evaluated in a first-in-human single-ascending dose study, and has now moved to a a multiple-ascending dose study.
The funding round was led by Deerfield Management and the AMR Action Fund, with additional investors like Illinois Ventures joining in.
There are currently four classes of antifungal drugs that are available, however they can come with problems such as antifungal resistance, organ toxicities, and drug-drug interactions. Invasive fungal infections typically affect people with compromised immune systems due to diseases such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, and organ transplants.
Elion’s candidate is a derivative of amphotericin, which has been used to treat fungal infections since the 1950s. However, Elion aims to curb kidney impairment – a common side effect caused by amphotericin – by increasing specificity to fungal cells.
Drug resistance in fungi was recently discussed at the 34th European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID) Global (formerly ECCMID) conference in Barcelona, Spain, in May 2024. A study – described at the conference – assessed the presence of resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Denmark, showing that the presence of the microorganism increased between 2020 and 2022 in both Danish soil and air.
According to the CEO of AMR Action fund Henry Skinner, the World Health Organization recently identified four fungal pathogens that it considers a 'critical priority,' including Aspergillus fumigatus.
In the announcement accompanying the funding, Elion’s chief medical officer Kieren Marr said: “Invasive fungal infections (IFI) have reached historic levels of concern, largely due to increased medical reliance on biologic immunosuppression, more people with severe pulmonary disease at risk of IFI, and increased exposures associated with environmental changes.”
Elion isn’t the only player in the fungal disease space. In December 2023, Astellas won FDA approval for the antifungal therapy Cresemba (isavuconazonium sulfate). The drug also gained FDA orphan drug exclusivity and pediatric market exclusivity for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis in March 2024.