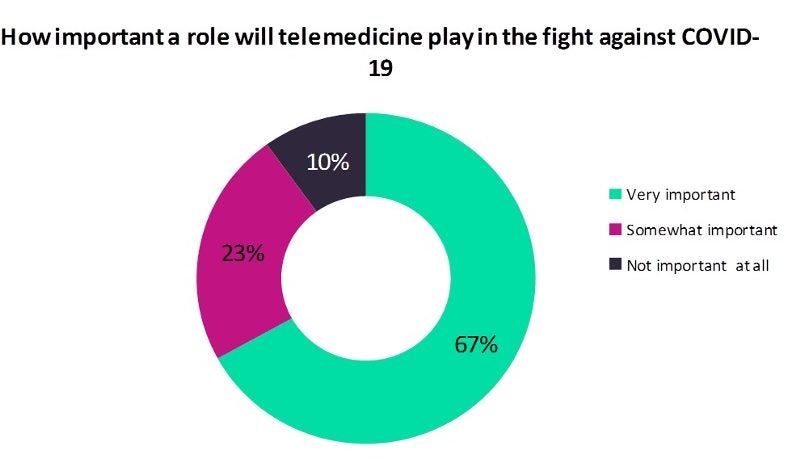
The COVID-19 pandemic has showcased how telemedicine can help in limiting exposure to the virus and curbing the disease spread. Verdict has conducted a poll to assess how important a role telemedicine will play in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic.
Analysis of the poll results shows that telemedicine will play a very important role in the fight against COVID-19, with a majority 67% of the respondents having opined that way.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
While 23% of the poll respondents felt that telemedicine will play a somewhat important role, a minority 10% voted that it will not play an important role at all.
The analysis is based on 853 responses received between 06 April and 20 April.

Telemedicine’s role in fighting COVID-19 outbreak
Telemedicine involves providing remote virtual healthcare services by healthcare providers from different locations. Despite the advantages, telemedicine has not been adopted widely.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe COVID-19 outbreak, however, has brought telemedicine to the forefront as governments urge the general public to use approved telemedicine facilities to seek treatment for mild symptoms instead of going to a hospital and risking exposure.
Patients who are self or home-isolated, patients with mild symptoms, and discharged patients are utilising the technology to remotely communicate with healthcare providers to receive treatment. This, in turn, reduces the pressure on emergency rooms and clinics enabling them to attend to more serious cases.
Telemedicine also helps in providing routine care to patients with underlying chronic conditions who are at high risk if they contract the virus. Further, healthcare providers who have been quarantined can provide treatment advice to patients remotely without the risk of infecting others.




