The pharmaceutical industry continues to be a hotbed of innovation, with activity driven by the evolution of new treatment paradigms, and the gravity of unmet needs, as well as the growing importance of technologies such as pharmacogenomics, digital therapeutics, and artificial intelligence. In the last three years alone, there have been over 633,000 patents filed and granted in the pharmaceutical industry, according to GlobalData’s report on Innovation in Pharmaceuticals: Nucleoside chemical synthesis. Buy the report here.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
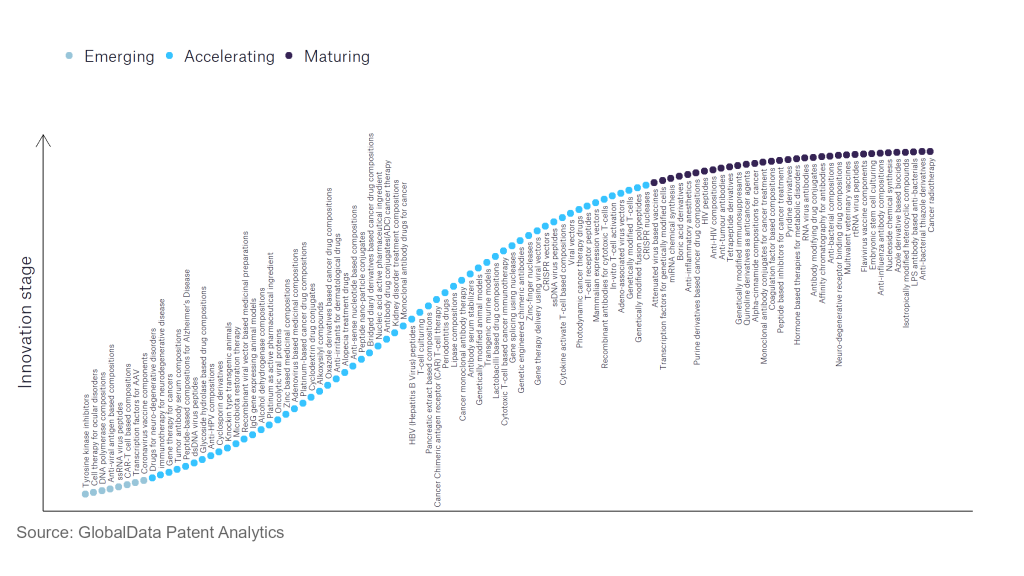
However, not all innovations are equal and nor do they follow a constant upward trend. Instead, their evolution takes the form of an S-shaped curve that reflects their typical lifecycle from early emergence to accelerating adoption, before finally stabilising and reaching maturity.
Identifying where a particular innovation is on this journey, especially those that are in the emerging and accelerating stages, is essential for understanding their current level of adoption and the likely future trajectory and impact they will have.
110 innovations will shape the pharmaceutical industry
According to GlobalData’s Technology Foresights, which plots the S-curve for the pharmaceutical industry using innovation intensity models built on over 756,000 patents, there are 110 innovation areas that will shape the future of the industry.
Within the emerging innovation stage, cell therapy for ocular disorders, coronavirus vaccine components, and DNA polymerase compositions are disruptive technologies that are in the early stages of application and should be tracked closely. Adeno-associated virus vectors, alcohol dehydrogenase compositions, and antibody serum stabilisers are some of the accelerating innovation areas, where adoption has been steadily increasing. Among maturing innovation areas are anti-influenza antibody compositions and anti-interleukin-1, which are now well established in the industry.
Innovation S-curve for the pharmaceutical industry
Nucleoside chemical synthesis is a key innovation area in the pharmaceutical industry
Nucleosides are typically synthesised by coupling nucleophilic pyrimidines, purines, or other basic heterocycles with an electrophilic ribose or deoxyribose derivative. Nucleosides can be synthesised from nucleophilic bases and electrophilic sugars by three general methods. The fusion method involves heating the base and acetyl-protected 1-acetoxyribose to 155 °C, resulting in a 70% yield of the nucleoside. The metal salt method involves the combination of a metal salt of the heterocycle with an enclosed sugar halide. The silyl-Hilbert-Johnson (SHJ) reaction is the combination of a silylated heterocycle and protected sugar acetate in the presence of a Lewis acid. Transglycosylation, which involves reversible transfer of a sugar moiety from one heterocyclic base to another, is also effective in converting pyrimidine nucleosides into purine nucleosides.
GlobalData’s analysis also uncovers the companies at the forefront of each innovation area and assesses the potential reach and impact of their patenting activity across different applications and geographies. According to GlobalData, there are 110 companies, spanning technology vendors, established pharmaceutical companies, and up-and-coming start-ups engaged in the development and application of nucleoside chemical synthesis.
Key players in nucleoside chemical synthesis – a notable innovation in the pharmaceutical industry
‘Application diversity’ measures the number of different applications identified for each relevant patent and broadly splits companies into either ‘niche’ or ‘diversified’ innovators.
‘Geographic reach’ refers to the number of different countries each relevant patent is registered in and reflects the breadth of geographic application intended, ranging from ‘global’ to ‘local’.
Gilead Sciences is the leading patent filer in nucleoside chemical synthesis. The company is engaged in the development and commercialisation of medicines for the treatment of cardiovascular, haematological and respiratory diseases, inflammation, liver diseases, and cancer. Emtricitabine (Emtriva), a synthetic nucleoside analogue of cytidine with anti-HIV activity developed by Gilead, has received approval in multiple geographies. The company sells its products through subsidiaries and distributors in Europe, the Americas, Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa.
Johnson & Johnson and Merck are the other key patent filers on nucleoside chemical synthesis.
In terms of application diversity, AstraZeneca is the top company, followed by C. H. Boehringer Sohn and Epigenetics Pharma. By means of geographic reach, Delta-Fly Pharma holds the top position. Changzhou Fangyuan Pharmaceutical and Eisai stand in second and third positions, respectively.
To further understand the key themes and technologies disrupting the pharmaceutical industry, access GlobalData’s latest thematic research report on Pharmaceutical.
Data Insights
From

The gold standard of business intelligence.
Blending expert knowledge with cutting-edge technology, GlobalData’s unrivalled proprietary data will enable you to decode what’s happening in your market. You can make better informed decisions and gain a future-proof advantage over your competitors.



