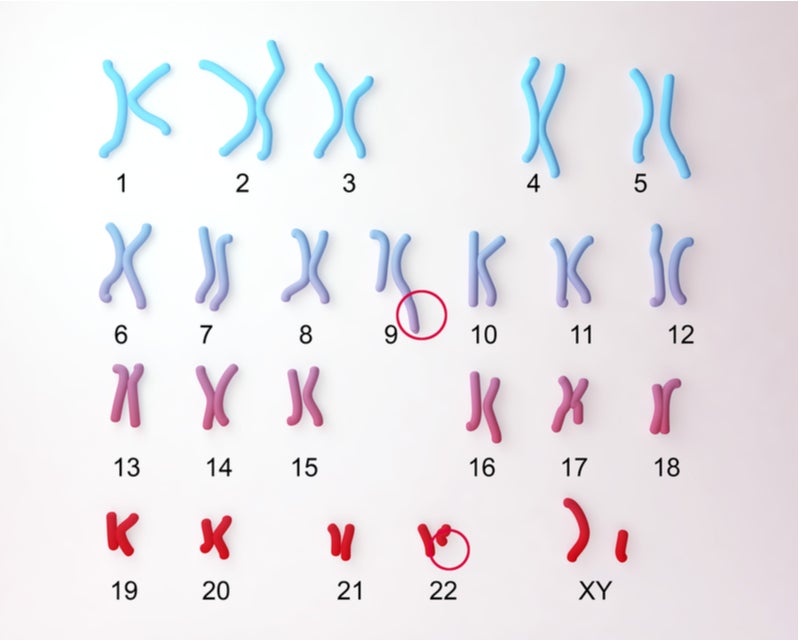
The Philadelphia chromosome (Ph) is the product of a chromosomal translocation that occurs between chromosomes 9 and 22. Ph contains the BCR-ABL fusion gene, which is the underlying cause of most chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) cases, 20–30% of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), and a minor proportion of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) cases.
Novartis’ Gleevac (imatinib mesylate) dramatically improved the survival of CML patients harbouring Ph. Prior to the discovery of this targeted therapy, patients diagnosed with CML had a poor prognosis with no effective treatments available. Imatinib mesylate is an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) analogue that blocks the activity of BCR-ABL by binding to its inactive site. Although imatinib mesylate also targets other naturally occurring tyrosine kinases, the drug is relatively safe and has few side effects.
Imatinib mesylate was the first tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating CML patients and has been used since 2001 with great success. Although this drug is widely effective, several mechanisms of resistance have since arisen in patients treated with imatinib mesylate, leading to the development of second- and third-generation TKIs.
Second- and third-generation TKIs currently approved to treat CML include dasatinib, nilotinib, bosutinib, and ponatinib. These drugs are more potent than imatinib mesylate, bind to both the inactive and active sites of BCR-ABL, are effective against a wider range of BCR-ABL mutations, and/or block additional TKIs that can promote cancer growth such as PDGFR, KIT, and SCR. While imatinib mesylate, dasatinib, nilotinib, and bosutinib are approved by the FDA for the treatment of newly diagnosed CML patients, ponatinib is only indicated for treating chronic, acute, or blast phase CML.
Sources indicate that global sales of patented Gleevac amounted to approximately $4.7bn in 2015. The patent for Gleevac expired in 2015, and generic imatinib mesylate drugs entered the US market in 2016. The entry of generic imatinib mesylate into the US market reduced the annual cost of imatinib mesylate treatment from more than $120,000 in 2015 to approximately $35,000 in 2019.
However, many experts feel that this price is still far too high, as notably lower prices for imatinib mesylate are available in Canada, Europe, and developing countries such as India.

US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataThe expiration of Gleevac’s patent for CML and the subsequent entry of generics into this drug market is likely to improve treatment options and thus the survival of CML patients worldwide. It will also likely exhibit a positive impact on the in vitro diagnostics market for BCR-ABL companion diagnostic testing.