Eli Lilly is building a pharmaceutical manufacturing facility in Durham County, North Carolina, US.
The company will produce injectable products and delivery devices, such as insulin pens for diabetes care, at the Durham facility.
In January 2020, Eli Lilly announced plans to invest up to $474m to develop the facility.
The construction phase will last for up to five years, with the facility expected to be operational by 2023.
Employment opportunities
The plant is expected to generate 462 jobs over five years. Eli Lilly will hire candidates in various roles, including scientists, manufacturing operations, quality professionals and engineers. Initial recruitment will take place in 2020, with the majority of the hiring anticipated for around 2023.
Employees’ average annual wage will be around $73,000, while the starting wages for entry-level jobs will be around $49,000.
Location of the new facility
Eli Lilly’s pharmaceutical manufacturing facility will be on the Parmer campus at the Research Triangle Park (RTP) in Durham, which lies across the TW Alexander Drive near the North Carolina Biotechnology Centre. The company bought 110 acres at Parmer for $36m in May 2020.
Research Triangle Park is a research and innovation centre managed by the Research Triangle Foundation, a not-for-profit organisation. It is equidistant from Raleigh, Durham and Chapel Hill.
Spanning 7,000 acres, it is the largest research park in the US and houses government organisations, academic institutes, non-profit organisations, start-ups and science and technology companies. Eli Lilly cited North Carolina’s workforce capabilities as the main reason for choosing the state over other states.
Eli Lilly manufacturing facility features
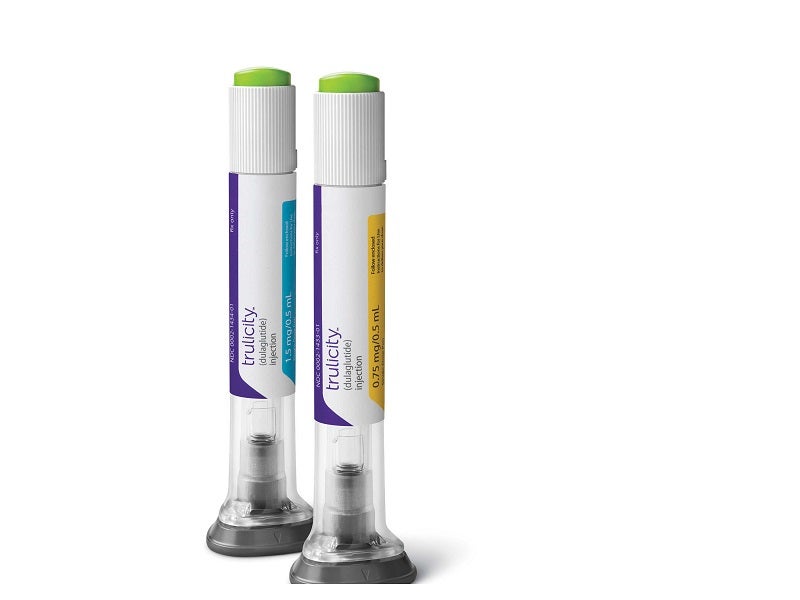
Developed as an integrated life science manufacturing factory, the facility will initially focus on manufacturing two diabetes drugs, Trulicity™ (dulaglutide) and tirzepatide.
Trulicity was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in 2014. Tirzepatide is a drug candidate being developed for diabetes patients with increased cardiovascular risk.
The facility will encompass new-age technologies such as robotics, automation and data analytics for managing tasks, including drug formulation. It will also cover filling and packaging tasks related to commercial and late-stage development drug candidates.
Financing and incentives for the Eli Lilly facility
Eli Lilly secured a Job Development Investment Grant (JDIG) from North Carolina for the development of the facility. Approved by the state’s Economic Investment Committee in January 2020, the 12-year grant will see the company receive a reimbursement of up to $8.7m, subject to the fulfilment of agreed investment and job creation targets.
During the grant period, the facility is expected to add $4.1bn to the state’s economy.
Under the JDIG agreement, around $2.8m would be moved into the state’s Industrial Development Fund-Utility Account to support rural communities in upgrading infrastructure.
Eli Lilly is also expecting to receive local incentives of up to $2.55m from Durham County. North Carolina Community Colleges will contribute $1.15m to provide personalised training support.
The Economic Development Partnership of North Carolina, Duke Energy, the NC General Assembly and the Greater Durham Chamber of Commerce are also supporting the project.
Marketing commentary on Eli Lilly
Eli Lilly is a US-based pharmaceutical company founded in 1876. The company focuses on the treatment of chronic illnesses such as cancer, autoimmune conditions, diabetes and Alzheimer’s.
In 1994, Eli Lilly bought Sphinx Pharmaceuticals, a spin-out of Duke University biochemistry lab, for roughly $76m.
In the 1990s, the company established a drug research centre in the Research Triangle Park. The facility generated more than 100 jobs before it closed in 2005.
Eli Lilly has manufacturing facilities, as well as research and development (R&D) amenities, in eight countries. The company markets its products in 120 countries.
Eli Lilly takes almost ten years to move a drug from the discovery stage to the patients, with a cost of around $2.6bn from discovery to development.
In January 2020, the FDA approved the company’s triple-combination diabetes drug, Trijardy™ XR, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.